Discover how AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs provide exceptional performance and energy efficiency for gaming, content creation, and everyday tasks. Explore the best models and their capabilities.
AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency
Table of Contents
In the rapidly evolving world of desktop computing, where demands for speed and performance are at an all-time high, AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency stands out as a beacon of innovation and reliability. Launched in 2020, this series marked a significant leap in AMD’s CPU technology, showcasing an impressive combination of power, efficiency, and affordability.
With an architecture that supports advanced computing needs, the Ryzen 4000 series has become a favorite among gamers, content creators, and everyday users alike. In this article, we will explore the architectural design, performance benchmarks, power efficiency, and practical applications of the AMD Ryzen 4000 series, demonstrating why it represents the perfect blend of power and efficiency.
1. Introduction to AMD Ryzen 4000 Series
The AMD Ryzen 4000 series features a lineup of processors based on the Zen 2 architecture, which utilizes a 7nm manufacturing process. This innovative technology allows these CPUs to deliver superior performance while maintaining lower power consumption, which is a fundamental aspect of the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency philosophy.
The Ryzen 4000 series includes a mix of traditional CPUs and Accelerated Processing Units (APUs) that integrate Radeon Vega graphics, catering to a wide range of users from gamers to professionals. With a focus on performance-per-watt, these processors enable users to experience high levels of computing power without the associated energy costs.
2. Architectural Advantages
The AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency is built upon several architectural enhancements over its predecessors. The following key features contribute to its success:
2.1. Zen 2 Architecture
At the core of the Ryzen 4000 series is the Zen 2 architecture. This architecture is renowned for its increased instructions per clock (IPC), which translates to higher performance in both single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks. By enhancing IPC, AMD has ensured that the Ryzen 4000 series can effectively handle a variety of workloads.
2.2. Unified Cache Design
The Ryzen 4000 series processors utilize a unified cache design, which integrates a larger L3 cache. This larger cache reduces memory latency and improves data access speeds, contributing to the overall efficiency of the CPU. The faster data retrieval from the cache allows the processor to perform better in various applications, particularly in gaming and productivity tasks.
2.3. Advanced Power Management
Power efficiency is a hallmark of the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency. AMD’s innovative power management features, such as Precision Boost and Smart Shift, dynamically adjust the CPU’s performance and power consumption based on the workload. This means that the processor can deliver maximum performance when needed while conserving energy during less demanding tasks.
3. A Diverse Lineup: CPUs and APUs
The AMD Ryzen 4000 series is designed to cater to a wide range of users, featuring both CPUs and APUs. Let’s take a closer look at the key models in this series:
3.1. Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs
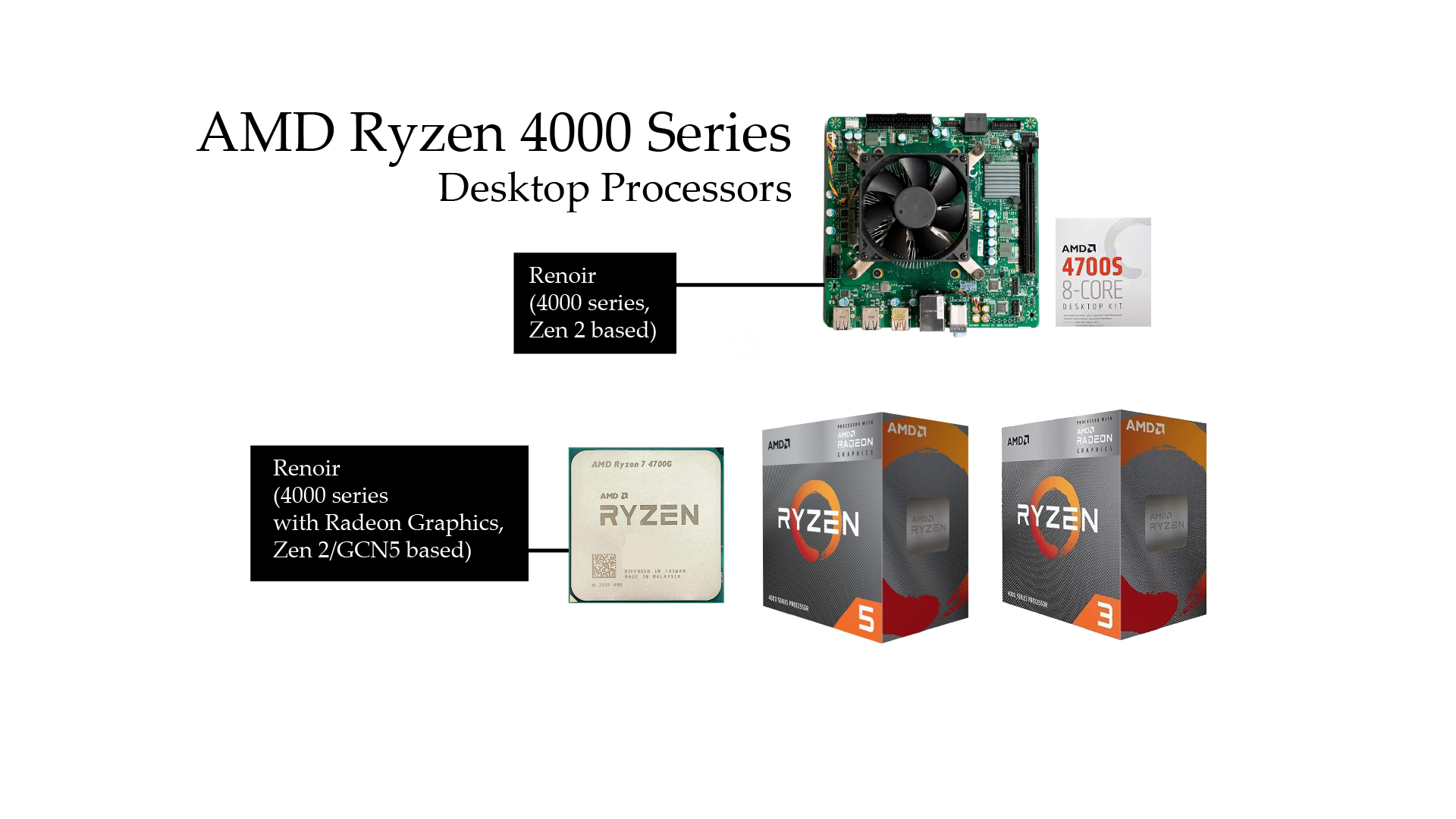
- Ryzen 5 4500: This 6-core, 12-thread processor is an excellent choice for mid-range gaming and productivity. It strikes a balance between performance and affordability, making it ideal for users who want solid performance without breaking the bank.
- Ryzen 3 4100: Designed for entry-level builds, the Ryzen 3 4100 features 4 cores and 8 threads. It delivers good performance for everyday tasks and light gaming, making it a great choice for budget-conscious users.
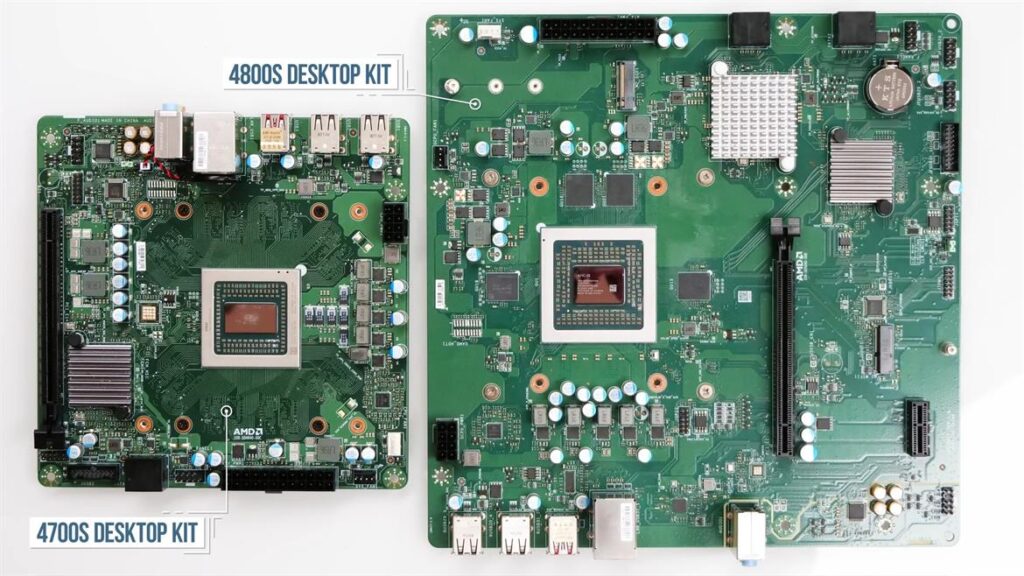
- AMD 4800S: Aimed at specialized systems, the AMD 4800S features 8 cores and 16 threads. It is tailored for specific applications and embedded systems, providing robust performance in compact setups.
- AMD 4700S: Similar to the 4800S, the 4700S is optimized for unique hardware configurations, offering reliable performance in custom builds where space is a constraint.
3.2. Ryzen 4000 Series APUs
- Ryzen 7 4700G: This 8-core, 16-thread APU combines powerful CPU performance with integrated Radeon Vega graphics. It is ideal for gamers and content creators who require high performance without the need for a dedicated GPU.
- Ryzen 7 4700GE: A power-efficient variant of the 4700G, the 4700GE maintains similar performance levels while consuming less power. It is perfect for compact builds where energy efficiency is a priority.
- Ryzen 5 4600G: With 6 cores and 12 threads, this APU offers a great balance of processing power and integrated graphics performance. It is suitable for most gaming and productivity tasks.
- Ryzen 5 4600GE: Like the 4700GE, the 4600GE is designed for energy efficiency, making it a great choice for users looking to build a quieter, cooler system.
- Ryzen 3 4300G: This entry-level APU features 4 cores and 8 threads, making it suitable for basic computing and light gaming. It offers excellent value for budget-oriented builds.
- Ryzen 3 4300GE: The power-efficient variant of the 4300G, this processor is optimized for lower energy consumption while still delivering solid performance.

Table Comparison of AMD Ryzen 3000 Series Desktop CPUs
| Category | Model | Cores/Threads | Base Clock | Boost Clock | Graphics (if any) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renoir (Zen 2 Based) | Ryzen 3 4100 | 4 / 8 | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | No | 65W |
| Ryzen 5 4500 | 6 / 12 | 3.6 GHz | 4.1 GHz | No | 65W | |
| AMD 4700S | 8 / 16 | 3.5 GHz | 4.2 GHz | No | 65W | |
| AMD 4800S | 8 / 16 | 3.2 GHz | 4.2 GHz | No | 65W | |
| Renoir (Zen 2/GCN5 Based) | Ryzen 3 4300G | 4 / 8 | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | Radeon Vega 6 | 65W |
| Ryzen 5 4600G | 6 / 12 | 3.7 GHz | 4.2 GHz | Radeon Vega 7 | 65W | |
| Ryzen 5 4600GE | 6 / 12 | 3.3 GHz | 4.0 GHz | Radeon Vega 7 | 35W | |
| Ryzen 7 4700G | 8 / 16 | 3.6 GHz | 4.4 GHz | Radeon Vega 8 | 65W | |
| Ryzen 7 4700GE | 8 / 16 | 3.2 GHz | 4.3 GHz | Radeon Vega 8 | 35W |
Key Notes:
- TDP: Thermal Design Power, indicating the maximum amount of heat generated by the processor that the cooling system must dissipate.
- Graphics: Refers to the integrated graphics capabilities provided by the CPU.
4. Performance Benchmarks
The AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency has been put to the test in various performance benchmarks across gaming, productivity, and power efficiency. Let’s delve into how these processors perform in real-world scenarios:
4.1. Gaming Performance
In gaming benchmarks, the Ryzen 4000 series delivers impressive results. The Ryzen 7 4700G, equipped with integrated graphics, showcases the ability to play popular titles smoothly at 1080p resolution. This capability makes it an excellent option for gamers who may not want to invest in a dedicated GPU.
The Ryzen 5 4500, on the other hand, provides exceptional performance when paired with a discrete graphics card, offering high frame rates in demanding games. Its combination of cores and threads allows for smooth multitasking, which is crucial for modern gaming experiences.
4.2. Productivity Performance
For content creators and professionals, the Ryzen 4000 series shines with its multi-core performance. The Ryzen 7 4700G excels in video editing, 3D rendering, and multitasking scenarios. Benchmarks reveal that it significantly reduces rendering times compared to previous generations, providing efficiency that can be a game-changer for creative workflows.
Even entry-level models, such as the Ryzen 3 4100, perform admirably in productivity applications. Whether it’s document editing, web browsing, or light photo editing, these processors handle everyday tasks with ease, emphasizing the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency ethos.
4.3. Power Efficiency
One of the standout features of the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency is their power consumption. With TDP ratings ranging from 35W to 65W, users can expect lower electricity costs while enjoying high performance.
The advanced power management features allow these CPUs to adjust their power consumption dynamically, ensuring that they deliver optimal performance without unnecessary energy usage. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in compact builds where thermal management is crucial.
5. Competitive Landscape
AMD’s rise in the CPU market can be attributed to the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency, which has effectively challenged Intel’s dominance in several key areas. Let’s explore how these processors stack up against their competitors.
5.1. Performance vs. Cost
One of the primary reasons users gravitate towards the AMD Ryzen 4000 series is its exceptional performance-to-price ratio. Compared to Intel’s offerings, Ryzen processors often provide superior multi-threaded performance at a lower price point.
This value proposition is particularly appealing to gamers and content creators, who need powerful processors without the premium price tag that often accompanies high-end Intel CPUs.
5.2. Compatibility and Upgrade Paths
Another significant advantage of the AMD Ryzen 4000 series is its compatibility with existing AM4 motherboards. This allows users to upgrade their processors without needing to invest in a new motherboard, further enhancing the cost-effectiveness of their builds.
Users can experience the benefits of the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency without the hassle of replacing multiple components, making it an attractive option for many.
6. Real-World Applications
The AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency caters to a diverse range of applications, making them suitable for various users. Here are some practical use cases for these processors:
6.1. Gaming Systems
For gamers, the Ryzen 5 4500 and Ryzen 7 4700G offer outstanding performance. These CPUs can easily handle modern games while providing the necessary horsepower for streaming and multitasking. The integrated graphics of the 4700G allow for casual gaming without the need for an additional GPU, making it a cost-effective option.
6.2. Content Creation Workstations
Content creators benefit from the multi-core capabilities of the Ryzen 4000 series. The Ryzen 7 4700G is ideal for video editing, graphic design, and other resource-intensive tasks. Its ability to handle multiple applications simultaneously enhances workflow efficiency, allowing creators to focus on their projects rather than waiting for rendering times.
6.3. Budget-Friendly Builds
For users on a budget, the Ryzen 3 4100 and 4300G provide excellent value. They are capable of handling everyday tasks, such as web browsing, word processing, and media consumption, without sacrificing performance. These processors allow users to build cost-effective systems that perform well in daily computing scenarios.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency is a testament to AMD’s commitment to innovation in the desktop processor market. With its advanced architecture, impressive performance, and energy-efficient design, the Ryzen 4000 series has set a new standard for what users can expect from their CPUs.
Whether you are a gamer looking for high frame rates, a content creator seeking faster rendering times, or a budget-conscious user wanting reliable performance for everyday tasks, the Ryzen 4000 series has something to offer. Its versatility, combined with exceptional value, ensures that it remains a top choice for a wide range of users.
As technology continues to advance, the AMD Ryzen 4000 Series CPUs Power Meets Efficiency will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of computing, making it a worthy consideration for anyone looking to upgrade or build a new system.




What i don’t understood is in truth how you’re not really much more smartly-favored than you may be now. You are very intelligent. You recognize thus considerably in the case of this topic, made me in my view imagine it from numerous various angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved unless it’s something to do with Girl gaga! Your individual stuffs great. Always care for it up!
thanks.